1.1 انواع زبان های برنامه نویسی
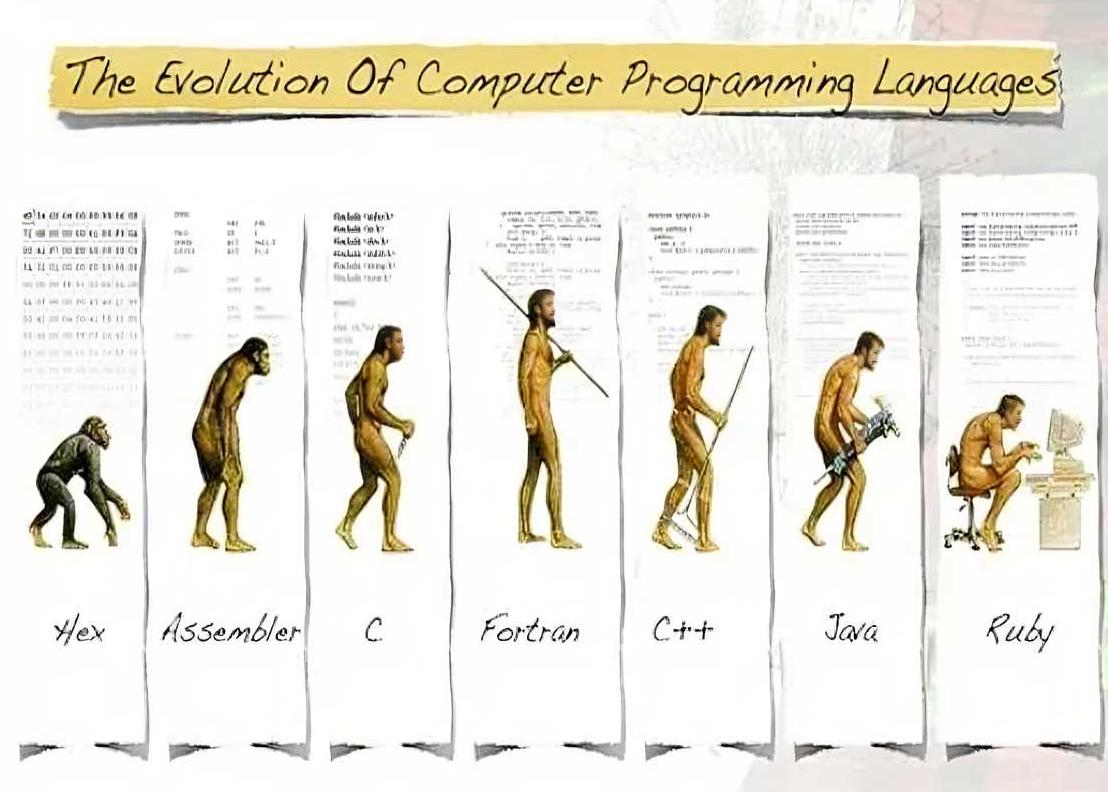
شکل 1.1: انقلاب زبانهای برنامه نویسی
- زبان انسان (English)
- زبانهای برنامه نویسی سطح بالا (C, C++, R, Python)
- زبان برنامه نویسی سطح پایین (Assembly)
- زبان ماشین (01)
نکته. در نهایت اکثر زبانهای برنامه نویسی منطق یکسانی دارند و یا دگیری یک زبان برنامه نویسی، یادگیری زبان برنامه نویسی دیگر را ساده تر میکند.
سایت تبدیل زبان برنامه نویسی R به زبان برنامه نویسی Assembly https://www.codeconvert.ai/r-to-assembly-converter
- خروجی
name Age
1 Mohsen 30
2 Arash 12- R
- Matlab
- Python
Code
- Sas
data df;
input name $ age;
datalines;
Mohsen 30
Arash 12
;
run;
proc print data=df;
run;- Fortran
PROGRAM main
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER :: i
CHARACTER(LEN=10), DIMENSION(2) :: name
INTEGER, DIMENSION(2) :: age
name(1) = "Mohsen"
name(2) = "Arash"
age(1) = 30
age(2) = 12
DO i = 1, 2
WRITE(*,*) "name: ", name(i), ", age: ", age(i)
END DO
END PROGRAM main- C
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
int main() {
std::vector<std::string> name = {"Mohsen", "Arash"};
std::vector<int> Age = {30, 12};
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<int>> df;
df["name"] = name;
df["Age"] = Age;
for (const auto& pair : df) {
std::cout << pair.first << ": ";
for (const auto& value : pair.second) {
std::cout << value << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}- Assembly
asm
.data
df_name_data:
.asciz "Mohsen"
.asciz "Arash"
df_age_data:
.int 30
.int 12
df_nrows = 2
df_ncols = 2
.text
.globl main
main:
# Allocate memory for the data frame
movl $df_nrows, %eax
movl $df_ncols, %ebx
imull %ebx, %eax
shl $2, %eax # Each element is 4 bytes (int)
pushl %eax
call malloc
popl %ecx
movl %eax, %edi # edi points to the data frame
# Copy the name data
movl $df_name_data, %esi
movl $0, %ecx
loop1:
cmpl $df_nrows, %ecx
je end1
movl (%esi), %eax
movl %eax, (%edi)
addl $4, %edi # Move to the next column
addl $4, %esi # Move to the next name
incl %ecx
jmp loop1
end1:
# Copy the age data
movl $df_age_data, %esi
movl $0, %ecx
loop2:
cmpl $df_nrows, %ecx
je end2
movl (%esi), %eax
movl %eax, (%edi)
addl $4, %edi # Move to the next column
addl $4, %esi # Move to the next age
incl %ecx
jmp loop2
end2:
# Print the data frame
movl $df_nrows, %eax
movl $df_ncols, %ebx
imull %ebx, %eax # Total number of elements
movl %edi, %ebx # ebx points to the start of the data frame
movl $0, %ecx
loop3:
cmpl %eax, %ecx
je end3
# Print the current element
pushl (%ebx)
pushl $format
call printf
addl $8, %esp
addl $4, %ebx # Move to the next element
incl %ecx
jmp loop3
end3:
# Free the memory
movl %edi, %eax
call free
xorl %eax, %eax
ret
.data
format:
.asciz "%d "